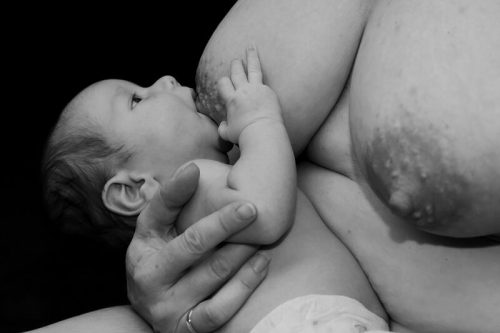
Breastfeeding is one of the most important practices a mother can do to ensure her baby’s health and development. Breast milk is the most complete food in the world, able to provide the newborn with everything necessary for development. Breastfeeding isn’t only beneficial for the baby; it also offers a series of advantages for the mother besides strengthening the mother-baby bond. The World Health Organization (WHO) recommends exclusive breastfeeding with only breast milk for the first six months of life, introducing other foods after this age but maintaining breastfeeding for the first two years of life. 
- How breastfeeding works
- Benefits of breastfeeding
- Lactational Amenorrhea Method (LAM)
- Best contraceptive methods for those who are breastfeeding
How breastfeeding works
Breastfeeding is a natural process of the body, common to all mammals. During pregnancy, but especially once the baby is born, the mother’s body starts to prepare to feed her baby. This process, in addition to involving various hormones, has a high caloric cost, requiring a lot of energy and resources, drawn directly from the mother’s body. Unlike what many people think, breast milk is not stored in the breast until it’s time for the baby to feed. In reality, the breast is a factory that produces milk, and its production occurs according to the baby’s demand. That is, the more the baby nurses, the more milk the mother will produce. How milk is produced During pregnancy, progesterone levels are very high, which, in addition to maintaining pregnancy, inhibits milk production. After birth, with the placenta expelled, these hormone levels drop and prolactin—the hormone responsible for milk production—begins to increase. The period from the placenta’s expulsion until milk “comes in” (lactogenesis) takes some time. For women who had a vaginal delivery, this time is usually up to 3 days, while for those who had a cesarean it can take up to 7 days. This difference happens because women who delivered vaginally have much higher oxytocin levels, which aids breastfeeding. While the milk hasn’t come in yet, women release a secretion (often during pregnancy) called colostrum. Colostrum is highly caloric and nutritious and should be the only food offered to the baby until milk comes in.
Benefits of breastfeeding
That breastfeeding is extremely beneficial for both baby and mother is almost universally known, but did you know these benefits begin right in the delivery room? When breastfeeding starts within the first hour of life, besides helping to establish the mother-baby bond, it aids in expelling the placenta and reduces the risk of postpartum hemorrhage. This happens because breastfeeding stimulates the release of oxytocin, the hormone responsible for uterine contractions.
Lactational Amenorrhea Method (LAM)
For many years, it was believed that the hormones released during breastfeeding were sufficient to suppress progesterone, thereby preventing ovulation. Based on this belief, the Lactational Amenorrhea Method (LAM) was developed, which consists of a contraceptive method based on breastfeeding. However, over the years, there is no conclusive scientific evidence to recommend using LAM as a contraceptive method, since there is no way to determine how long a postpartum woman will go without menstruating and the influence of factors related to breastfeeding, sexual activity, diet, and others are unknown.
Examining current literature, we can say that practicing the Lactational Amenorrhea Method as a contraceptive is not recommended.
Contraceptive methods for those who are breastfeeding
Many women stop using contraceptive methods, especially hormonal ones, after giving birth because they believe that using them can harm the baby and breastfeeding. While the use of hormone-based methods (mainly estrogen) is not recommended, there are other ways to prevent an unwanted pregnancy.
- Copper IUD
- Male and female condoms
- Diaphragm
- Withdrawal
- Fertility awareness
- Vasectomy
There are some hormonal contraceptives that can be used alongside breastfeeding, but before starting any of them, consult your gynecologist to ensure that use will not harm breastfeeding. Now that you know how breastfeeding works and the relationship between its hormones and fertility, you surely understand why it is possible to get pregnant while breastfeeding. So, if you want to avoid a new pregnancy, always remember to use a non-hormonal contraceptive method during sexual intercourse. Breastfeeding is good for your health, but it is not enough to prevent ovulation from occurring.