Children are fragile beings who easily catch diseases. It’s not uncommon to see hospitals full of children with different types of viruses, which is quite understandable, since their immune systems are still developing. All of this is part of life and hardly any of these viruses will cause serious harm to a child’s development. There are countless diseases that are more common in little ones. This is the case for otitis, chickenpox, mumps, and also hand, foot, and mouth disease, which is rarer than the others mentioned but is much more common among children. But after all, how can you identify this disease? What are its causes? What dangers does it bring to children’s health? Let’s talk more deeply about this.
What is hand, foot, and mouth disease?
It is also called HFMD, its abbreviation in English, and is caused by a virus called Coxsackie1, from the enterovirus family, the same group that causes the well-known stomatitis. The vast majority of cases occur in children under 5 years of age, although it can also affect older children and even adults. It is a highly contagious disease and, because of this, it tends to spread quickly among children who are together, such as in daycare centers or among siblings, for example.
Causes of hand, foot, and mouth disease
Hand, foot, and mouth disease is mainly transmitted through saliva and, because it is very contagious, even minimal contact can be enough for transmission to occur2. In addition to sharing utensils, cups, or food being very common causes of Coxsackie transmission, simply coughing near someone or having skin contact with contaminated saliva can cause someone to contract hand, foot, and mouth disease. Because it can also be transmitted through feces, a person who uses the bathroom and doesn’t wash their hands properly may end up passing the disease on to others. This transmission usually occurs in the first week that the person is infected. However, babies can carry the virus in their stool for longer, even for months after having contracted the virus. That’s why it is always important to be cautious about contamination, even after the person is already cured.
Main symptoms of hand, foot, and mouth disease
The virus can have an incubation period of one to seven days. The disease brings several symptoms that can be confused with those of other illnesses. Some of the main symptoms of hand, foot, and mouth disease are:
- Sore throat
- Difficulty swallowing
- Loss of appetite
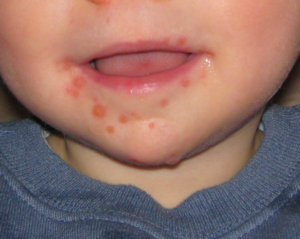
- Blisters in the mouth, mainly inside
- Blisters on the feet and hands
- Blisters on the genitals
- Drowsiness
- Fever
- Malaise
- Weight loss
It is very common for some of these symptoms to be mistaken for those of a simple cold, which can make it hard for doctors to give the correct diagnosis so that treatment can begin quickly. That makes it important to pay attention to the most characteristic symptoms of the disease, such as eruptions in the mouth, hands, and soles of the feet. It’s good to remember that infection with the virus does not always cause all the symptoms. Sometimes only the blisters prevail, or sometimes only the sore throat and fever. That’s why you should pay attention so it isn’t treated incorrectly.
Treatment of the disease
A doctor should be sought when parents suspect that it is not just a common cold. This is normal when the fever is very high, when the blisters are very evident, or when symptoms like drowsiness or weight loss are present. Unfortunately, there isn’t a direct treatment to combat the virus. What is done is to fight the symptoms to relieve pain and fever. Within a few days, signs of improvement become very evident, but there are some things that can be done to make the process even more efficient:
- Keep the child always hydrated
- Make sure to give the child foods that are easy to swallow
- Keep the child at rest
- Always wash hands after dealing with infected children
These simple measures make fighting the disease even more effective and help keep the process from being painful for children.
Possible complications
When not properly treated, hand, foot, and mouth disease can cause symptoms such as rising fever, little urine output and dark-colored urine, increased blisters that may even produce pus, and excessive drowsiness. These complications are mainly due to lack of hydration. In rare and very severe cases, the disease can lead to more dangerous illnesses, such as myocarditis, meningitis, or encephalitis3. But it is important to stress that this happens only in cases where there are several complications and is very rare. As you can see, hand, foot, and mouth disease is not the deadliest nor the most dangerous. However, it is a disease that spreads easily and can cause a lot of inconvenience in our lives. It is always important to stay calm when our kids catch a virus or some unfamiliar disease, because often the treatment is simple and almost painless. Showing calmness and confidence to your child is important so that they feel calm and secure about what is happening. Follow medical guidance and you will see that the disease will be cured in a short time. See also: Vomiting in Children. When Is It a Warning Sign? Photo: MidgleyDJ a