Understanding ovulation isn’t just a topic for women who are trying to conceive; understanding how your own body works is the subject of an intelligent, modern woman who takes care of herself. Knowing how your body functions and recognizing the signs of each change during the menstrual cycle greatly helps women both to get pregnant more easily and to prevent pregnancy.
What is Ovulation?
Ovulation is the name of one of the phases of the menstrual cycle, a phase of extreme importance for the continuation of life. It is at this moment that the egg is released by the ovaries in order to be fertilized by a sperm and thus generate an embryo. This phase of the cycle occurs during the much anticipated fertile window, which is the moment when pregnancy is most likely. When this released egg is not fertilized, the process of shedding the uterine lining begins and menstruation occurs.
How to Know the Exact Day of Ovulation?
As we mentioned, ovulation happens during the fertile period and the calculation may vary depending on the length of a woman’s cycle. For example, considering that a woman has a regular 28-day cycle, her fertile period will be on the 14th day (halfway through the cycle). Since the body can undergo natural changes due to hormonal variations, instead of considering this 14th day as the only fertile day, we consider the 3 days before and 3 days after as having greater probability within the fertile week. However, we don’t need to rely solely on calendar dates. It is possible to track through body changes whether ovulation is about to happen or is actually happening.
Symptoms of Ovulation
The functioning of the female body is so extraordinary that each month, with every menstrual cycle, the body adapts itself for the renewal of the cycle, the preparation to receive an embryo, and its complete elimination so everything can begin anew. And to receive this embryo, the body also prepares itself to facilitate the arrival of sperm through increased vaginal moisture and discharge. This is one of the ovulation symptoms and is something that women can easily observe. The presence of vaginal mucus that looks like raw egg white, slippery, is the well-known sign of ovulation, helping sperm reach the mature egg. With these changes, libido also increases, making intercourse even more pleasurable. Other common symptoms that women report during ovulation are little twinges on one side of the abdomen, similar to mild cramps. This discomfort is related to the moment when the mature egg is released and the sensitivity of some women to feel this exact moment.
IMPORTANT: Ovulation pain usually lasts a few minutes or hours and does not occur in every cycle.
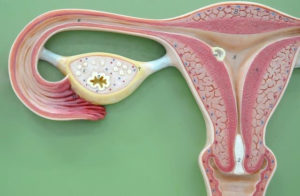
How Does Ovulation Occur?
The process of ovulation happens only once in each menstrual cycle. As this moment approaches, the hormone estrogen increases its production, which helps reinforce and strengthen the lining of the inner walls of the uterus, preparing to host a future embryo to be developed. This increase in estrogen causes a rise in another hormone, LH (luteinizing hormone), which is responsible for releasing the mature egg. The lifetime of this mature egg is up to 24 hours, and if it is not fertilized within this period, it is expelled along with the uterine lining during menstruation, when a new cycle will begin.
Late Ovulation
Since the human body is not a machine, unexpected changes can happen, especially in cases of hormonal imbalances. And, what many women don’t know is that late ovulation can indeed occur. This provides a consistent explanation for women who claim to have gotten pregnant outside the fertile period —in reality, they were indeed ovulating, just later than usual. Even women with highly regular menstrual cycles can experience this due to a hormonal fluctuation. With this in mind, we can say that the rhythm method is not reliable as a contraceptive, since there can be cycle variations and late ovulation can occur.
Ovulation Tests
For those trying to get pregnant and wanting to be sure they are ovulating in order to maximize their chances, ovulation tests are the best method, aside from being attentive to the signals the body sends. Ovulation tests were developed to help women confirm their ovulatory period, providing better accuracy and increasing the chances of getting pregnant more quickly. Ovulation tests are small strips, similar to pharmacy pregnancy tests. Using a small urine sample, preferably collected in the late afternoon, the sensitive tip of the ovulation test can detect the levels of LH (luteinizing hormone) in the urine, indicating the approach of ovulation or if it is actually happening. To make ovulation testing easier, if a woman knows her menstrual cycle well and knows the estimated ovulation days, the test will simply serve as confirmation, making it easier to identify the fertile window.
Is There Ovulation Without Mucus?
One of the main signs of ovulation is cervical mucus, but not all women can easily distinguish or identify it. In some cases, a woman may not have much mucus at all, or it may be so little that it goes unnoticed. But even if there is no visible mucus, ovulation is still happening. The best way to confirm ovulation in these cases is to observe the other symptoms that the body presents during this period, and of course, track your fertile calendar as it approaches. In these cases, using an ovulation test can be very helpful, as it will confirm ovulation even without apparent mucus.
How to Increase Ovulation Mucus?
If your body produces little ovulation mucus, some helpful steps can stimulate its production. Drinking water is essential, and if you already drink a lot of water, try to drink even more. Another great tip is to eat yams, whether as food, powder, capsules, or even tea. Yams contain properties that boost ovulatory function and thus increase the production of ovulation mucus, making it more resilient and noticeable. This makes it easier to identify ovulatory periods and also aids conception. For couples trying to conceive, another valuable tip for women with little mucus is to use fertility-friendly gel lubricants such as FamiGel. In addition to fulfilling the role of female mucus, it helps the sperm by increasing their mobility until they reach the egg.
Ovulation Inducers
For women who want to become pregnant and find it difficult to detect ovulation—either because it doesn’t occur or because their cycle is irregular—the gynecologist may prescribe ovulation inducers to help conception. Ovulation inducers are medications made from clomiphene citrate and may also be prescribed for women with PCOS (polycystic ovary syndrome) who want to get pregnant. But it’s important to note that even though this is a very effective treatment, there are side effects. Therefore, their use must be prescribed by a doctor and properly monitored. Incorrect use can cause severe pain due to ovarian stimulation, or even ovarian hyperstimulation, overloading the ovary and causing intense pain. In extreme cases, removal of the ovary affected by hyperstimulation may be necessary. That’s why you should never use these medications without medical prescription and supervision. If it is determined that ovulation is not happening at all, the gynecologist may order evaluation tests to check your hormone levels. Blood tests measuring LH, FSH, prolactin, progesterone, and especially estrogen are essential to reach the correct diagnosis and treatment. In many cases, lack of ovulation can be easily resolved, or it may be just a simple hormonal imbalance responsible for making the cycle irregular.











